Leadership Competencies Analysis - A Study with Reference to Women Managers in Software Industry
Leadership Competencies of Women Managers
The nature of leadership specifically impacts the wellbeing and
achievement of each organization. Leaders regularly have the insight, encounter
and interpersonal aptitudes required to effectively lead an organization, yet
it is the comprehension of how to apply that information that defines
competence. To comprehend the particular leadership competencies of woman
managers they were made a request to rate their competencies. The reason here
is to comprehend the leadership competencies. From the accessible information
the variable investigation was led and the respondents are tried for respond
and the information was dissected. The KMO (Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin) esteem is
touched base at 0.531, since it is more prominent than 0.05 and is appropriate
for conducting factor analysis. Therefore the factor analysis was conducted.
The extricated shared traits among 100 respondents and observed to be least of
0.543 for precise self management and maximum of 0.909 for Interprets and
communicates business. For understanding
the dimensionality of leadership competencies that are key for the Managerial
development. The 29 factors are reduced to 10 components.
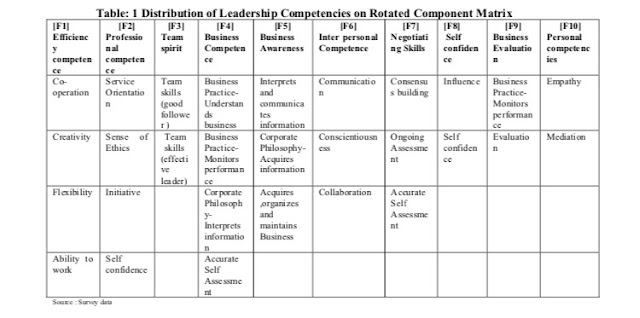
According to Table 1, the factors stacked on pivoted segment grid are
Co-operation, Creativity, Flexibility and Ability to deal with (F1) part which
is named as Efficiency Competence. The factors stacked on the (F2) part are
service orientation, sense of ethics, Initiative, self-confidence which is
named as professional competence. The factors stacked on (F3) are Team skills (good
follower), Team skills (effective leader) which are named as Team spirit. The
factors stacked on the (F4)
business practice, corporate
philosophy, accurate self assessment which is named as Entrepreneurial
competence. The variables stacked on the (F5) segment are Interprets &
communication, corporate philosophy which is named as business awareness. The
factors stacked on the (F6) part are Communication, Conscientiousness and
Collaboration which is named as Social competence. The factors stacked on the
(F7) segment are Consensus building, On-going Assessment, Accurate self
assessment. The factors stacked on the (F8) part are Influence, Self confidence
which is named as Self confidence. The factors stacked on the (F9) part are
Business practice-monitors performance which is named as Business evaluation.
The factors stacked on the (F10) part are Empathy and mediation which is named
as personal competence. Women Managers who are having these blends are candidly
mindful and are solid in leadership behaviour.
From Table 2, the factors stacked on turned part framework are
Co-operation, Ongoing Assessment, Flexibility, Creativity and Ability to work
and are stacked on (F1) segment which is named as Efficiency competence. The
factors stacked on the (F2) part are Positive point of view, Conscientiousness,
Service orientation, Initiative, Empathy and Communication which is named as
professional competence. The factors stacked on (F3) are Business practice
understanding and monitoring and corporate philosophy which is named as
Business competence. The factors stacked on the (F4) part are Team skills being
an effective leader and Team leader being a good follower which is named as
Team spirit. The factors stacked on the (F5) segment are interprets and
communicates information, Acquires, organizes and maintains Business and
Corporate Philosophy-Acquires data which are named as Business Awareness.
Ladies Managers who are having these mixes are candidly mindful and are solid.
Comparison of Factors Loaded on Rotated Component Matrix
The elements stacked on turned segment framework are decreased to 10
elements and 5 figure every emphasis. These elements are given a name in light
of the competencies which are classified. The competencies are regular in both
the cases; they are Efficiency competence, Professional competence, Business
competence, Team spirit, Business awareness. This empowers us to presume that
women managers are having leadership competencies which are vital for the
business basic leadership. Furthermore, the vital leadership competency
clusters are clarified in the accompanying figure-1.
Analysis of variance between the means of leadership competencies and Age
and Experience of the respondents
With a specific end goal to analyse whether there is noteworthy change
emerging between the methods for leadership competencies and Age and
Experience, ANOVA is led. The outcomes demonstrate that there is huge
difference between the mean for Efficiency competencies (0.05) and age yet
there is no critical variety between means for Professional Competence (0.951),
Business Competence (0.408), Team Spirit (0.358), and Business Awareness
(0.262). There is huge fluctuation between the methods for Business Awareness
(.053) and encounter however there is no noteworthy variety between means for
Efficiency competence (0.767), Professional Competence (0.98), Business
Competence (0.321), Team Spirit (0.439). Efficiency competence and Business
awareness are the two vital important leadership competencies which are
essential for the leadership development and women managers have these
qualities which help them to be effective managers in organisations. At the
point when women managers with great relationship building abilities have the
solid fearlessness and are adjusting with the changing business situation and
take choices as needs be and prove their dynamism they will be effective.





Comments
Post a Comment